Difference between revisions of "C4Dキャピラリー電気泳動による飲料水のカチオンおよびアニオンの同時分析"
(→Introduction) |
(→はじめに) |
||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
最適な分析方法は、検出及び定量測定の特異性、直線性、精度、限界の条件を基に検証されたものです。さらに、この方法は51箇所の飲料水(国内の源泉)に含有する無機イオンの評価にも効果的に適用され、その多変量データ解析法を用いて飲料水の組成とその地理的起源との相関関係を解明しました。 | 最適な分析方法は、検出及び定量測定の特異性、直線性、精度、限界の条件を基に検証されたものです。さらに、この方法は51箇所の飲料水(国内の源泉)に含有する無機イオンの評価にも効果的に適用され、その多変量データ解析法を用いて飲料水の組成とその地理的起源との相関関係を解明しました。 | ||
| − | + | 測定のオリジナル研究者:Ioan Ovidiu Neaga, Bogdan Cezar Iacob and Ede Bodoki at the Iuliu Hatieganu University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Romania | |
== Equipment Required == | == Equipment Required == | ||
Revision as of 18:37, 26 May 2014
C4D 検出器を使ったキャピラリー電気泳動法による飲料水に含まれる標準的な10種類の無機イオン(アンモニア、カリウム、ナトリウム、カルシウム、マグネシウム、リチウム、塩素、硝酸塩、硫酸塩、及び硝酸塩)を同時モニターし定量測定しました。[1]
はじめに
eDAQ 社の C4D を Agilent G1600 キャピラリー電気泳動システムと組み合わせて行ったものです。測定のデザインは (DoE)、最適な条件 (最短の分析時間内に最大の感度と選択性を示す)が得られるように広範かつ迅速なアプローチを実施し構築したもので、結果として全イオンの分離測定時間は3分程度に収まりました。
最適な分析方法は、検出及び定量測定の特異性、直線性、精度、限界の条件を基に検証されたものです。さらに、この方法は51箇所の飲料水(国内の源泉)に含有する無機イオンの評価にも効果的に適用され、その多変量データ解析法を用いて飲料水の組成とその地理的起源との相関関係を解明しました。
測定のオリジナル研究者:Ioan Ovidiu Neaga, Bogdan Cezar Iacob and Ede Bodoki at the Iuliu Hatieganu University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Romania
Equipment Required
- C4D hardware unit, either:
- ER225 C4D Data System including PowerChrom software or
- ER815 C4D Detector with third-party data acquisition system
- ET120 C4D Headstage
- Agilent G1600 capillary electrophoresis system
Working Conditions
- Known sample: aqueous solution containing 15 ppm ammonium carbonate, 15 ppm potassium nitrate, 15 ppm calcium chloride, 10 ppm magnesium chloride, 10 ppm lithium sulfate, 15 ppm sodium nitrite
- Buffer: 15 mM pyromellitic acid, 10 mM citric acid, 2 mM 18-crown-6 ether adjusted at a pH of 3.70 with histidine
- CE Instrument:
- Separation voltage +30 kV
- Capillary: PVA coated fused silica capillary
- Total length 60 cm, effective length 18 cm
- Outer diameter 360 μm, internal diameter 50 μm
- Sample injection: hydrodynamic, dual opposite end injection; First the sample was injected at the inlet applying a pressure of 500 mbar, followed by the second injection at the outlet, applying a negative pressure of 50 mbar for 5 seconds at the inlet
- C4D settings: frequency 1000 kHz; amplitude 100%; headstage gain: ON
- Data recording: low-pass filter: 5 Hz; range: 50 mV; sampling rate: 1000 data points per second with the aid of Chart v.5.5.8 software
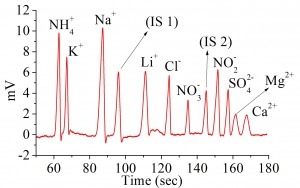
Results
The electropherogram is shown in Figure 2. The limits of detection and limit of quantifications are shown in the table below.
| Ion | NH4+ | K+ | Na+ | Li+ | Cl- | NO3- | NO2- | SO42- | Mg2+ | Ca2+ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LODc (mg/L) | 1.54 | 0.45 | 0.075 | 0.094 | 2.51 | 0.92 | 0.076 | 0.901 | 0.44 | 2.33 |
| LOQc (mg/L) | 4.67 | 1.39 | 0.22 | 0.28 | 7.62 | 2.80 | 0.23 | 2.73 | 1.33 | 7.08 |
Reference
[1] The analysis of small ions with physiological implications using capillary electrophoresis with contactless conductivity detection; Ioan Ovidiu Neaga, Bogdan Cezar Iacob, Ede Bodoki; Journal of Liquid Chromatography & Related Technologies; manuscript accepted 11th July 2013