Difference between revisions of "C4Dキャピラリー電気泳動を用いた無機陽イオン検出"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
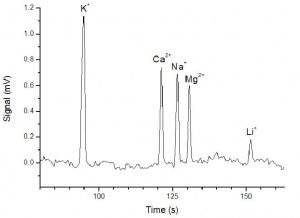
[[File:Electropherogram of 10 uM inorganic cations.jpg|300px|thumb|right|10 µM の無機陽イオンのエレクトロフェログラム]] | [[File:Electropherogram of 10 uM inorganic cations.jpg|300px|thumb|right|10 µM の無機陽イオンのエレクトロフェログラム]] | ||
| − | ''eDAQ C4D | + | ''eDAQ C4D システムはキャピラリー電気泳動によるカリウム、カルシウム、ナトリウム、マグネシウム、リチウムなどの無機陽イオンの検出に使われています。 '' |
== '''はじめに''' == | == '''はじめに''' == | ||
| − | + | スイスのバーゼル大学では自前のキャピラリー電気泳動The (CE) 装置に eDAQ C4D システムを組み込み、K<sup>+</sup>, Ca<sup>2+</sup>, Na<sup>+</sup>, Mg<sup>2+</sup> 及び Li<sup>+</sup> のなどの陽イオンを分析しています。 The method used was similar to experiments previously published: Comparison of Different Contactless Conductivity Detectors for the Determination of Small Inorganic Ions by Capillary Electrophoresis; Pavel Kubáñ, Christopher J. Evenhuis, Mirek Macka, Paul R. Haddad, Peter C. Hauser; Electroanalysis 18, 2006, No. 13-14, 1289 – 1296 | |
== Conditions == | == Conditions == | ||
Revision as of 12:26, 21 February 2014
eDAQ C4D システムはキャピラリー電気泳動によるカリウム、カルシウム、ナトリウム、マグネシウム、リチウムなどの無機陽イオンの検出に使われています。
はじめに
スイスのバーゼル大学では自前のキャピラリー電気泳動The (CE) 装置に eDAQ C4D システムを組み込み、K+, Ca2+, Na+, Mg2+ 及び Li+ のなどの陽イオンを分析しています。 The method used was similar to experiments previously published: Comparison of Different Contactless Conductivity Detectors for the Determination of Small Inorganic Ions by Capillary Electrophoresis; Pavel Kubáñ, Christopher J. Evenhuis, Mirek Macka, Paul R. Haddad, Peter C. Hauser; Electroanalysis 18, 2006, No. 13-14, 1289 – 1296
Conditions
- Sample: A solution of 10 µM of potassium, calcium, sodium, magnesium and lithium, dissolved in water.
- Buffer: 12 mM histidine and 50 mM acetic acid
- Instrument:
- separation voltage = 30 kV
- recorded separation current = 11 – 12 µA
- Capillary:
- fused-silica from Polymicro Technologies
- outer diameter = 360 µm
- internal diameter = 50 µm
- length = 60 cm
- length to detector = 50 cm
- Injection: gravity siphoning at 10 cm for 15 seconds
- C4D settings
- frequency = 800 kHz
- amplitude = 80 A
- headstage gain OFF
- Data recording:
- lowpass filter = 2 Hz
- range = 10 mV
- sampling rate = 1000 data points per second
Data and Limit of Detection
The figure shows the electropherogram for the 10 µM sample of inorganic cations. From this electropherogram, it can be estimated that the limit of quantitation (LOQ) of potassium, calcium, sodium and magnesium is 1 µM, and that of lithium is 3 µM. The limit of detection (LOD) is thus 0.3 µM for potassium, calcium, sodium and magnesium, and 1 µM for lithium.