Ionophores in Society
Ionophores are not only chemically interesting in their own right but have important medical and economic roles in our society.
A selection of ionophores is presented below for study in mainstream chemistry courses as well as courses for pre-med, vet, pharma, biochemistry, and soil and agricultural science students.
The use of ionophore 'growth promoters' in the animal feedstock industry is also of concern to environmental chemists because of their presence in manure and sewerage sludges used as fertiliser for human and animal crops.
The ability of these materials to transport ions across phospholipid bilayer cell membranes, which is usually the key to understanding their mode of action, can be easily studied using tethered membrane technology.
Contents
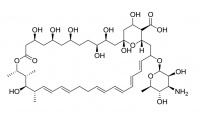
Amphotericin B
Amphotericin B is an antibiotic used to treat serious fungal infections. It forms ion channels in the fungal cell membrane with the assistance of ergosterol which is a naturally occurring lipid in fungal membranes. As a medicine it is administered intravenously as a liposomal preparation.
While its affinity for ergosterol makes it target fungal cells, Amphotericin can also interact, though to a lesser extent, with the cholesterol in mammalian cells. This limits its therapeutic dosage because of toxicity.
Amphotericin B is similar both in structure and in action to Nystatin.
Reference
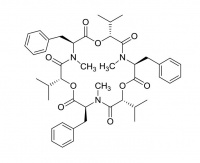
Beauvericin
Beauvericin is closely related to the macrocyclic enniatins, having three benzyl groups in place of the aliphatic chains of the enniatins. It is a potentially toxic agent found in grain crops affected by fungus.
Reference
- Occurrence of Beauvericin and Enniatins in Wheat Affected by Fusarium avenaceum Head Blight. A. Logrieco, A. Rizzo, R. Ferracane, and A. Ritieni, Applied Environmental Microbiology, 68, 82-85, 2002. DOI: 10.1128/AEM.68.1.82-85.2002
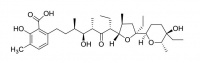
Calcimycin
The most notable feature of Calcimycin is ability to transport divalent cation across cell membranes. It affinity for cations is Ni2+ > Co2+ > Zn2+ > Mn2+ > Mg2+ ~ Ca2+ > Sr2+ > Ba2+, however transport rates across lipsomal membranes are reported as Cd2+ > Zn2+ > Ca2+ > Mg2+ > Sr2+ > Ba2+.
It has antibiotic properties, and is also being used in IVF treatments.
References
- Structures and Properties of Naturally Occurring Polyether Antibiotics. Jacek Rutkowski and Bogumil Brzezinski, BioMed Research International, Article ID 162513, 2013. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/162513
- Equilibria between ionophore A23187 and divalent cations: stability of 1:1 complexes in solutions of 80% methanol/water. CJ Chapman, AK Puri, RW Taylor, DR Pfeiffer, Biochemistry, 26, 5009-5018, 1987. DOI: 10.1021/bi00390a019
- The specificity of ionophore A23187 in cation transport across lipid membranes. Studies with lecithin vesicles. WG Pohl, R Kreikenbohm, K. Seuwen, Z Naturforsch C, 35, 562-568, 1980.
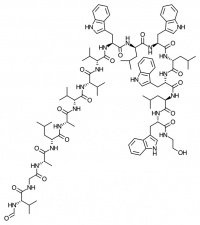
Gramicidin
Gramicidin is used as a topical antibiotic. It is often regarded as the archetypal ion channel despite its unusual dimer arrangement that can form across the cell membrane. It was one of the first commercially available antibiotics.
Gramicidin is usually sold as a mixture of related linear polypeptides (principally A, B and C) by Sigma-Aldrich and many other suppliers. The main component is Gramicidin A.
Gramicidin S is an unusual macrocyclic variant.
Reference
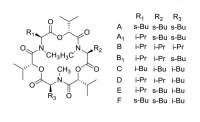
Enniatin complex
Enniatins are produced by fungal species that commonly infect wheat and other grains. High levels are potentially toxic.
A complex mixture of macrocylic molecules is commonly encountered. At last count there were 28 enniatins known.
There have also been some reports of Enniantins having promise as antibiotics and anti-cancer drugs..
Reference
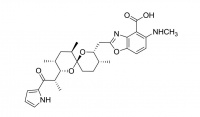
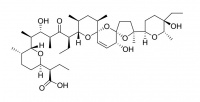
Lasalocid
Lasalocid is commonly used as an antibiotic for control of coccidiosis, a protozoan parasite of poultry and livestock.
Reference
Maduramicin
Maduramicin is used as an antibiotic for control of coccidiosis, a protozoan parasite of poultry and livestock.
Reference
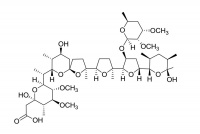
Monensin A
Monensin is used in the livestock industry as a food supplement, where it can alter the gut flora (bacteria populations) of the animal so that animal growth rates are improved.
References
- Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point (HACCP) Manual, Bio Agri Mix LP.
- Drug Information Online.
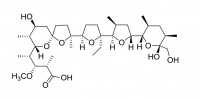
Narasin
Narasin is a methylated derivative of salinomycin, and has similar properties.
References
Nystatin
Nystatin is an antifungal antibiotic often prescribed for the treatment of Candida infections. It forms ion channels in the fungal cell membrane with the assistance of ergosterol which is a naturally occurring lipid in fungal membranes. As a medicine Nystatin is taken orally or topically.
While its affinity for ergosterol makes it target fungal cells, it can also interact, though to a lesser extent, with the cholesterol in mammalian cells. This can limit its therapeutic dosage because of toxicity.
It is similar both in structure and in action to Amphotericin B.
References
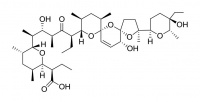
Salinomycin
Salinomycin is used in the livestock industry as a food supplement, where it can alter the gut flora (bacteria populations) of the animal so that animal growth rates are improved.
It is also being investigated as an anti-cancer agent.
References
- Persistence of antibiotics such as macrolides, tiamulin and salinomycin in soil. Michael P. Schlüsener, Kai Bester, Environmental Pollution, 143, 565–571, 2006. DOI: 10.1016/j.envpol.2005.10.049
- Effects of the veterinary pharmaceutical salinomycin and its formulation on the plant Brassica rapa. V. Furtula, G. L. Stephenson, K. M. Olaveson, P. A. Chambers, Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 63, 513-522, 2012. DOI: 10.1007/s00244-012-9807-y
- Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point (HACCP) Manual, Bio Agri Mix LP.
- SACOX Product Information Sheet, Invert Inc.
- Drug Information Online.
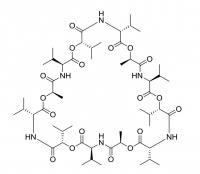
Valinomycin
Valinomycin is a macrocylic polypeptide and is historically one of the best known ionophores, especially for its 104 fold selectivity for potassium over sodium ions. It is being investigated for use as an antibiotic.
It is used in the manufacture of potassium ion selective electrodes.