Difference between revisions of "Analysis of Antioxidants using Cyclic Voltammetry"
(→Antioxidants in the Cosmetics Industry) |
(→Antioxidants in Cosmetics) |
||
| (13 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
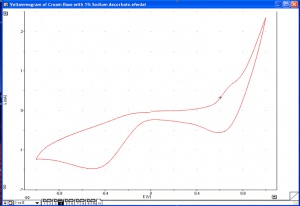
| − | [[File:Cv of cosmetic cream base with sodium ascorbate.jpg|300px|thumb|right|CV of | + | [[File:Cv of cosmetic cream base with sodium ascorbate.jpg|300px|thumb|right|Figure 1. CV of a cream base with 1.0% sodium ascorbate.]] |
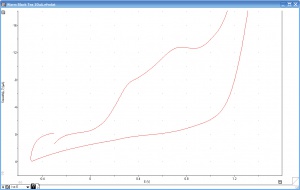
| − | [[File:Cv of warm black tea 20uA.jpg|300px|thumb|right|CV of Black Tea]] | + | [[File:Cv of warm black tea 20uA.jpg|300px|thumb|right|Figure 2. CV of Black Tea]] |
''The EChem Startup System can be used to analyse antioxidants using Cyclic Voltammetry'' | ''The EChem Startup System can be used to analyse antioxidants using Cyclic Voltammetry'' | ||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
Cyclic voltammetry (CV) is used in evaluating antioxidants in the oil, food, diagnostic and agricultural industries. | Cyclic voltammetry (CV) is used in evaluating antioxidants in the oil, food, diagnostic and agricultural industries. | ||
| − | CV is a rapid technique | + | CV is a rapid technique for measuring antioxidant levels and often requires minimal sample preparation. An electrode has an applied voltage is swept between two values. The current generated by the loss of electrons from the antioxidants leads to peaks in the current signal at given voltages. The voltage at which these peaks occur indicates the type of antioxidant, while the current peak height and area reflect the amount of antioxidant present. |
| − | == Antioxidants in | + | == Antioxidants in Cosmetics == |
| − | Antioxidants are a key | + | Antioxidants are often a key ingredient in many skin care products. They are claimed to provide protection against exposure to pollution and UV radiation, to repair skin damage and to have anti-aging effects, Quantifying the level of antioxidants in cosmetic raw materials allows the formulator to choose adjust the level of protection offered by the product. |
| − | Cyclic voltammetry is an affordable, robust tool for measuring the antioxidant capacity of plants, extracts, and formulations. In addition to its role in research, it is well suited for collecting quality control data and optimising extraction procedures. It is a simple way to measure and document the antioxidant capacity of a given substance. Figure 1 shows the voltammogram of | + | Cyclic voltammetry is an affordable, robust tool for measuring the antioxidant capacity of plants, extracts, and formulations. In addition to its role in research, it is well suited for collecting quality control data and optimising extraction procedures. It is a simple way to measure and document the antioxidant capacity of a given substance. Figure 1 shows the voltammogram of a cream base with 1.0% sodium ascorbate. |
| − | == Antioxidants in | + | == Antioxidants in Food == |
| − | The EChem Startup System has been used to perform cyclic voltammetry on a range of beverages. Figure 2 shows the antioxidant peaks in the cyclic voltammogram of black tea. | + | Many foodstuffs contain high levels of antioxidants. In fruit juices and plant extracts the main antioxidants are vitamin C (ascorbic acid), and an array of polyphenolic compounds. 'Staleness' of a food is often due to gradual oxidation (by air) leading to loss of the antioxidants, and monitoring of the 'total antioxidant level' in a foodstuff is often an indicator of its freshness and quality. 'Total antioxidant level' is usually quoted by referencing back to an equivalent amount of vitamin C (in aqueous samples) or vitamin E (for fat soluble antioxidants). The EChem Startup System has been used to perform cyclic voltammetry on a range of beverages. Figure 2 shows the antioxidant peaks (due to polyphenolic tannins) in the cyclic voltammogram of black tea. |
| − | Antioxidants in | + | |
| − | CV with the EChem Startup System | + | == Antioxidants in Medicine == |
| + | |||
| + | CV with the EChem Startup System can be used for the analysis of antioxidant levels in blood plasma, which can be used to determine the effects of diet, stress, and infection in suitable animal models. Antioxidant levels can also be quantified in traditional medicines. | ||
Latest revision as of 10:57, 11 August 2014
The EChem Startup System can be used to analyse antioxidants using Cyclic Voltammetry
Contents
Introduction
Cyclic voltammetry (CV) is used in evaluating antioxidants in the oil, food, diagnostic and agricultural industries.
CV is a rapid technique for measuring antioxidant levels and often requires minimal sample preparation. An electrode has an applied voltage is swept between two values. The current generated by the loss of electrons from the antioxidants leads to peaks in the current signal at given voltages. The voltage at which these peaks occur indicates the type of antioxidant, while the current peak height and area reflect the amount of antioxidant present.
Antioxidants in Cosmetics
Antioxidants are often a key ingredient in many skin care products. They are claimed to provide protection against exposure to pollution and UV radiation, to repair skin damage and to have anti-aging effects, Quantifying the level of antioxidants in cosmetic raw materials allows the formulator to choose adjust the level of protection offered by the product.
Cyclic voltammetry is an affordable, robust tool for measuring the antioxidant capacity of plants, extracts, and formulations. In addition to its role in research, it is well suited for collecting quality control data and optimising extraction procedures. It is a simple way to measure and document the antioxidant capacity of a given substance. Figure 1 shows the voltammogram of a cream base with 1.0% sodium ascorbate.
Antioxidants in Food
Many foodstuffs contain high levels of antioxidants. In fruit juices and plant extracts the main antioxidants are vitamin C (ascorbic acid), and an array of polyphenolic compounds. 'Staleness' of a food is often due to gradual oxidation (by air) leading to loss of the antioxidants, and monitoring of the 'total antioxidant level' in a foodstuff is often an indicator of its freshness and quality. 'Total antioxidant level' is usually quoted by referencing back to an equivalent amount of vitamin C (in aqueous samples) or vitamin E (for fat soluble antioxidants). The EChem Startup System has been used to perform cyclic voltammetry on a range of beverages. Figure 2 shows the antioxidant peaks (due to polyphenolic tannins) in the cyclic voltammogram of black tea.
Antioxidants in Medicine
CV with the EChem Startup System can be used for the analysis of antioxidant levels in blood plasma, which can be used to determine the effects of diet, stress, and infection in suitable animal models. Antioxidant levels can also be quantified in traditional medicines.