Analysis of Antioxidants using Cyclic Voltammetry
The EChem Startup System can be used to analyse antioxidants using Cyclic Voltammetry
Contents
Introduction
Cyclic voltammetry (CV) is used in evaluating antioxidants in the oil, food, diagnostic and agricultural industries.
CV is a rapid technique, compared to traditional techniques, for measuring antioxidants and often requires less sample preparation. As the applied voltage is swept between two values, the currents generated by the sample’s oxidation and reduction reactions are measured. The addition of antioxidants leads to changes in the voltammogram: Peaks at given voltages reflect the ability of the mixture to donate electrons as reducing agents.
Antioxidants in the Cosmetics Industry
Antioxidants are a key anti-aging ingredient in today’s cosmetic formulations. They provide reparative benefits and afford protection against exposure to pollution and UV radiation. Quantifying the level of antioxidant protection in cosmetic raw materials can allow the formulator to choose the exact level of protection suited to the application.
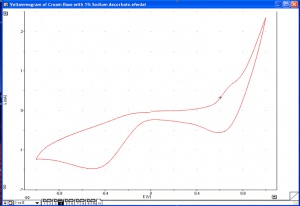
Cyclic voltammetry is an affordable, robust tool for measuring the antioxidant capacity of plants, extracts, and formulations. In addition to its role in research, it is well suited for collecting quality control data and optimising extraction procedures. It is a simple way to measure and document the antioxidant capacity of a given substance. Figure 1 shows the voltammogram of Cream Base with 1.0% sodium ascorbate.
Antioxidants in the Food Industry
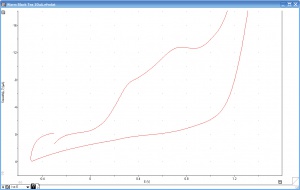
The EChem Startup System has been used to perform cyclic voltammetry on a range of beverages. Figure 2 shows the antioxidant peaks in the cyclic voltammogram of black tea.
Antioxidants in the Medical Industry
CV with the EChem Startup System has been used for the analysis of antioxidants in blood plasma. It was used to test if a diet high in antioxidants would lead to high concentrations of antioxidants in the blood plasma.