Difference between revisions of "Signal Sources and Amplifiers"
(→Single ended - Floating) |
|||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
===Single ended - Floating=== | ===Single ended - Floating=== | ||
| − | + | It works like this... Single Ended Floating signals which are not electrically connected to ground. The signal appears between the two terminals of the signal source. This signal can either be a voltage source or a current source. | |
An ideal voltage source has a near zero internal impedance - a battery for example. A pH electrode is a voltage source but this has a very high internal resistance. An accurate reading can only be obtianed with a measuring circuit whose own internal resistance is much higher than the source resistance of the source. Voltmeters therefore need to have a high internal reistance - ideally infinite. | An ideal voltage source has a near zero internal impedance - a battery for example. A pH electrode is a voltage source but this has a very high internal resistance. An accurate reading can only be obtianed with a measuring circuit whose own internal resistance is much higher than the source resistance of the source. Voltmeters therefore need to have a high internal reistance - ideally infinite. | ||
Revision as of 17:44, 13 September 2013
Contents
Introduction
In order to record an experimental signal with high fidelity 3 issues need to be considered.
- Signal Sources to be measured
- Characteristics of the signal sources
- Type of Amplifier used to record the signal
Signal Sources
There are 4 types or classes of electical signal sources which occur in various experimental situations. It is important to understand the characteristcs of these signal sources in order that they can be matched to the correct amplifier/recording system without degrading the accuracy of the measurement.
PLEASE NOTE: In discussing the characteristics of signal sources reference will be made to "Source Impedance" which in its most general form consists of a combination of 3 electrical elements: Resistance,Inductance and Capacitance. In most cases one of these elements will predominate, most commonly resistance. So when the term "Source Resistance" is used it implies that the impedance of the source is mainly resistive in nature. At DC or low frequencies source impedance is mainly resistive and the other elements, capacitance and inductance only come into play at higher frequencies.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electrical_impedance
These 4 classes are listed and discussed below:
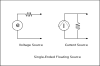
Single ended - Floating
It works like this... Single Ended Floating signals which are not electrically connected to ground. The signal appears between the two terminals of the signal source. This signal can either be a voltage source or a current source.
An ideal voltage source has a near zero internal impedance - a battery for example. A pH electrode is a voltage source but this has a very high internal resistance. An accurate reading can only be obtianed with a measuring circuit whose own internal resistance is much higher than the source resistance of the source. Voltmeters therefore need to have a high internal reistance - ideally infinite.
An ideal current Source has a near infinite internal impedance - a solar cell. In this case to measure the source current the measurment impedance should be very low. Ammeters therefore need to have a low internal resistance - ideally zero.
Here is a picture:
Single ended - Grounded with Common mode voltage
blah blah blah
Balanced - Floating
blah blah blah
Balanced - Grounded with Common mode voltage
blah blah blah
Source Characteristics
- Source Impedance
- Source Voltage
- Source Frequency content
Amplifier types
- Single ended - Grounded
- Single ended - Isolated
- Balanced - Grounded
- Balanced - Isolated